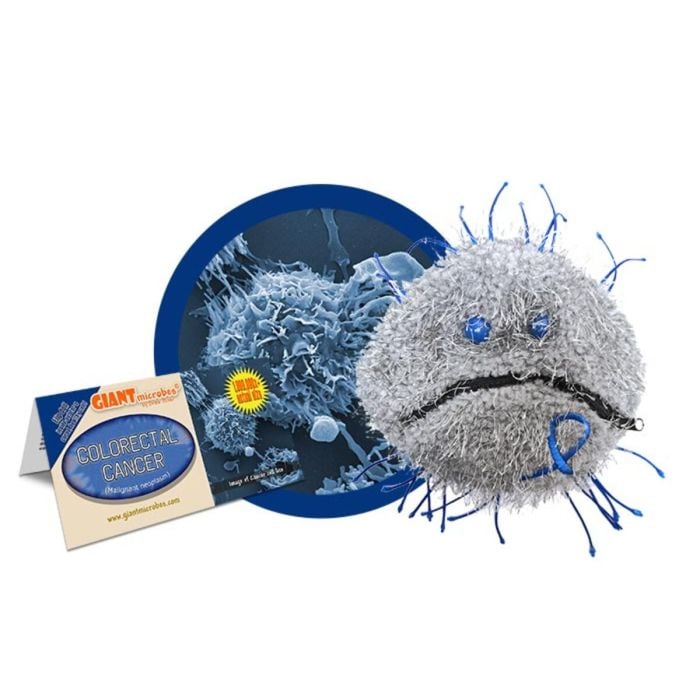
Colorectal Cancer (Malignant neoplasm)
Our Cancer cell can be "cured" by flipping it inside-out!
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 16-24" XL (XL) 10-15" Original (PD) 5-8" Keychain (KC) 2-4" with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Colorectal Cancer (Malignant neoplasm)
FACTS: The term cancer applies to more than 100 different diseases, all of which have two things in common. As a result of genetic damage, normal cells become cancerous and can grow in an uncontrolled manner. In addition, these cells are able to invade other tissues, disrupting and destroying the structures and organs that they infiltrate.
As with most cancers, colorectal cancers develop due to genetics as well as risk factors including poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and lack of exercise. Although the fundamentals of treatment - surgery, radiation and chemotherapy - have not changed in many years, advances in imaging, diagnosis, and sophisticated methods for delivering therapies have greatly improved their effectiveness. In addition, breakthroughs in immunotherapy are now being put into practice. As a result, many who develop cancer have a greatly improved chance of recovery compared to a few decades ago.
Colorectal cancer starts in the colon or the rectum. Colon cancer and rectal cancer are often grouped together as they have many features in common. Colorectal cancer often starts with the development of benign polyps, small clumps of cells that can turn cancerous. Polyps usually do not produce noticeable symptoms, which is why it is so important for those at high cancer risk (or anyone over the age of 50) to have regular screening tests such as a colonoscopy. Signs of colorectal cancer may include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool and discomfort in the abdomen.
The causes of colorectal cancer remain unclear. Risk factors include those shared with other types of cancer, as well as having had radiation treatment in your abdominal area to treat previous cancers.